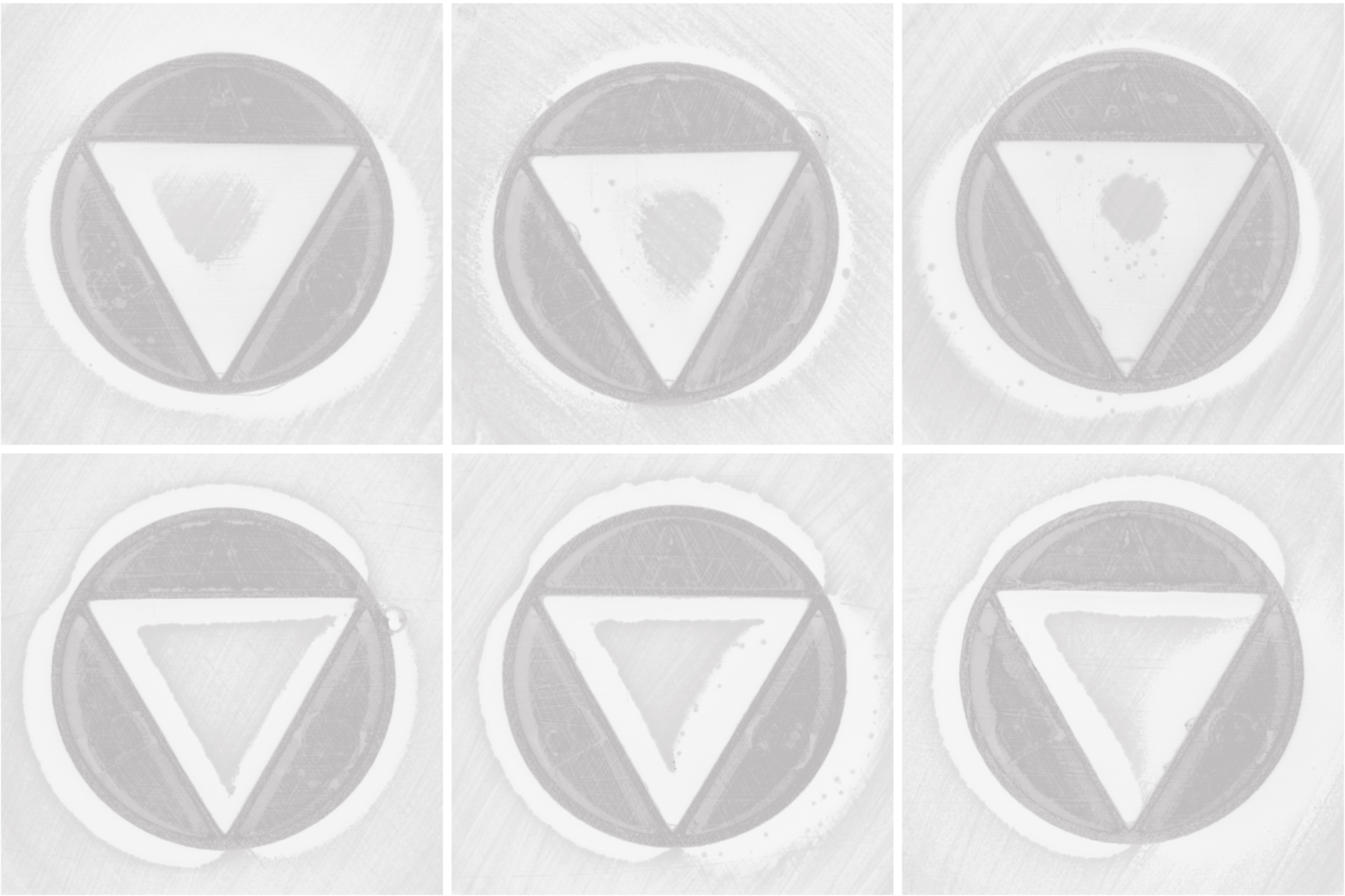
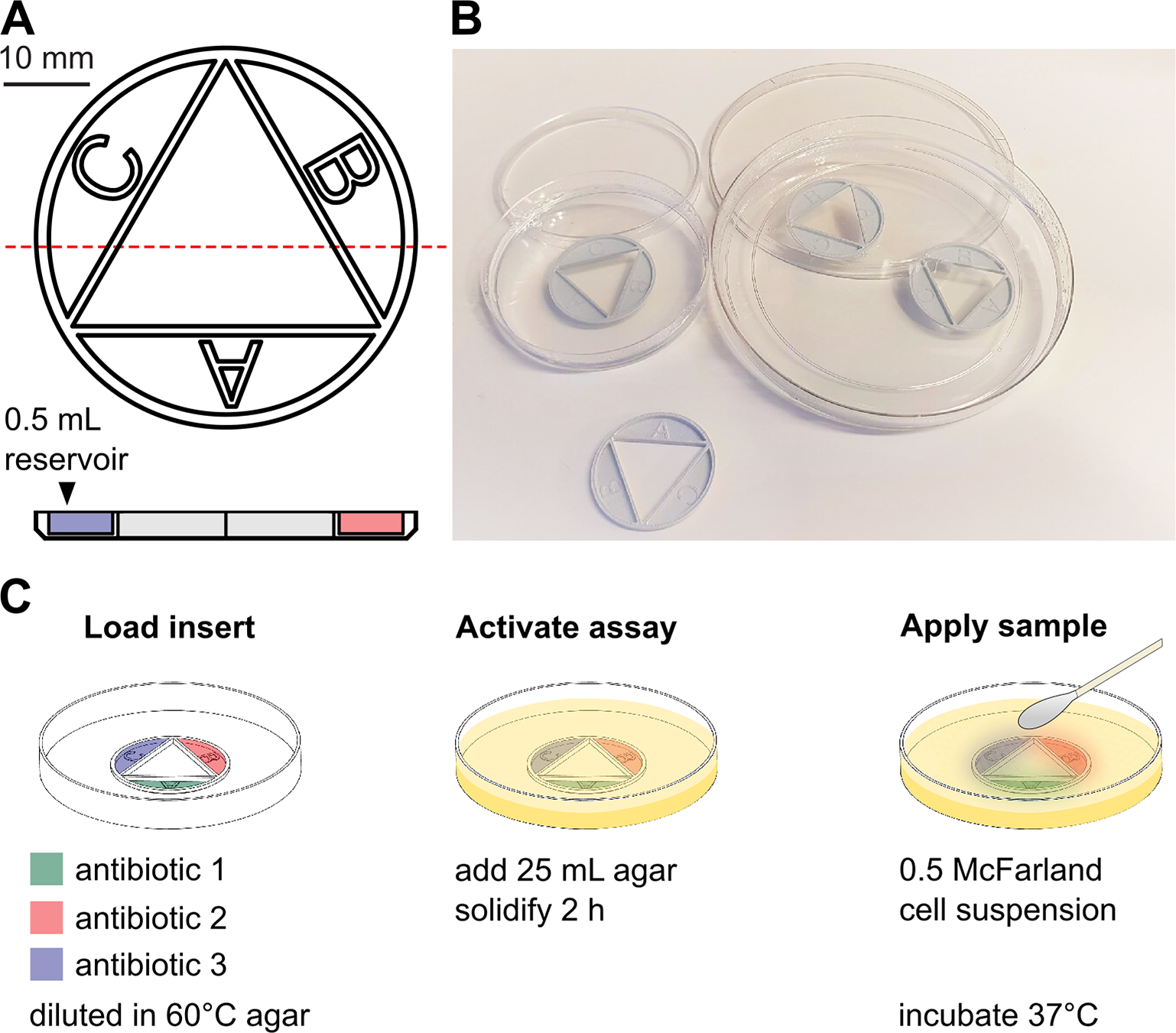
Antibiotic combination therapies are important for the efficient treatment of many types of infections, including those caused by antibiotic-resistant pathogens. Combination treatment strategies are typically used under the assumption that synergies are conserved across species and strains, even though recent results show that the combined treatment effect is determined by specific drug–strain interactions that can vary extensively and unpredictably, both between and within bacterial species. To address this problem, we present a new method in which antibiotic synergy is rapidly quantified on a case-by-case basis, allowing for improved combination therapy. The novel CombiANT methodology consists of a 3D-printed agar plate insert that produces defined diffusion landscapes of 3 antibiotics, permitting synergy quantification between all 3 antibiotic pairs with a single test.
Continue reading “CombiANT: Antibiotic interaction testing made easy”Within-species variability of antibiotic interactions in Gram-negative bacteria
Treatments with antibiotic combinations are becoming increasingly important even though the supposed clinical benefits of combinations are, in many cases, unclear. Here, we systematically examined how several clinically used antibiotics interact and affect the antimicrobial efficacy against five especially problematic Gram-negative pathogens. A total of 232 bacterial isolates were tested against different pairwise antibiotic combinations spanning five classes, and the ability of all combinations in inhibiting growth was quantified. Descriptive statistics, principal component analysis (PCA), and Spearman’s rank correlation matrix were used to determine the correlations between the different combinations on interaction outcome. Several important conclusions can be drawn from the 696 examined interactions. Firstly, within a species, the interactions are in general conserved but can be isolate-specific for a given antibiotic combination and can range from antagonistic to synergistic. Secondly, additive and antagonistic interactions are the most common observed across species and antibiotics, with 87.1% of isolate-antibiotic combinations being additive, 11.6% antagonistic, and only 0.3% showing synergy. These findings suggest that to achieve the highest precision and efficacy of combination therapy, not only isolate-specific interaction profiling ought to be routinely performed, in particular to avoid using drug combinations that show antagonistic interaction and an expected associated reduction in efficacy, but also discovering rare and potentially valuable synergistic interactions.
Read more: Within-species variability of antibiotic interactions in Gram-negative bacteriaIMPORTANCE
Antibiotic combinations are often used to treat bacterial infections, which aim to increase treatment efficacy and reduce resistance evolution. Typically, it is assumed that one specific antibiotic combination has the same effect on different isolates of the same species, i.e., the interaction is conserved. Here, we tested this idea by examining how several clinically used antibiotics interact and affect the antimicrobial efficacy against several bacterial pathogens. Our results show that, even though within a species the interactions are often conserved, there are also isolate-specific differences for a given antibiotic combination that can range from antagonistic to synergistic. These findings suggest that isolate-specific interaction profiling ought to be performed in clinical microbiology routine to avoid using antagonistic drug combinations that might reduce treatment efficacy.
Potential risks of treating bacterial infections with a combination of β-lactam and aminoglycoside antibiotics: A systematic quantification of antibiotic interactions in E. coli blood stream infection isolates
Full study on Lancet eBioMedicine
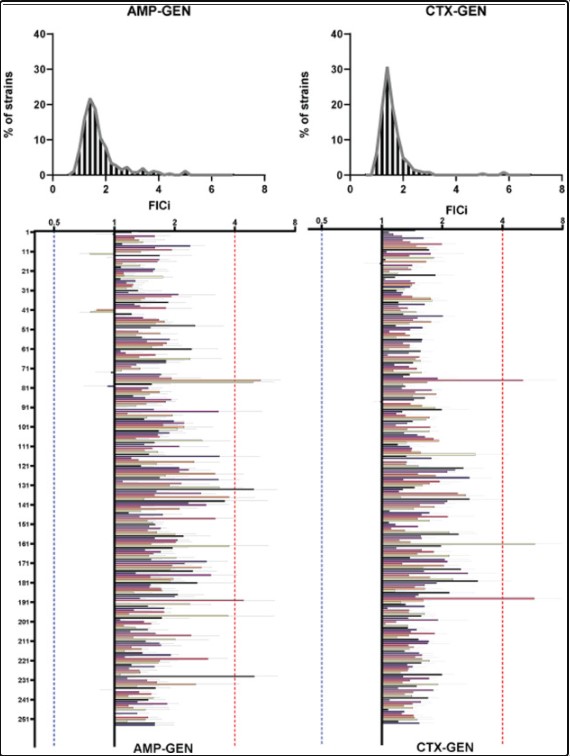
Treatment of Blood Stream Infections (BSIs) with a combination of a β-lactam and an aminoglycoside antibiotic is widely used in intensive care units (ICUs) around the world. However, no studies have systematically examined how these drugs interact and potentially influence the antimicrobial efficacy of the overall treatment. We collected 500 E. coli isolates from the Uppsala University hospital that were isolated from blood of patients with suspicion of infection. Of those we tested the efficacy of combinations of 2 common β-lactam antibiotics (Ampicillin and Cefotaxime) combined with 2 common aminoglycosides (Gentamicin and Tobramycin) on 254 isolates. The efficacy of all 4 pairwise combinations in inhibiting bacterial growth was then examined on all susceptible strains. That was done by quantifying the Fractional Inhibitory index (FICi), a robust metric for antibiotic combinatorial behaviour, of all possible treatments on every strain. When non additive interactions were identified, results of the original screen were verified with time kill assays. Finally, combination behaviours were analysed for potential cross correlations.
Continue reading “Potential risks of treating bacterial infections with a combination of β-lactam and aminoglycoside antibiotics: A systematic quantification of antibiotic interactions in E. coli blood stream infection isolates”